Advantages of Vertical Color Mixers with Helical Stirring in Comparison to Other Mixing Techniques
In the world of plastic processing and color masterbatch blending, achieving a uniform, efficient, and contamination-free mix is essential to maintaining product quality and production consistency. Among the various equipment used for this purpose, the Vertical Color Mixer stands out, especially when utilizing a spiral (or screw-type) mixing mechanism. This method has gained prominence due to its practical advantages over alternative mixing technologies, such as paddle or tumble mixers. Understanding the benefits of spiral mixing within these machines helps manufacturers make better-informed decisions about their blending solutions.

The spiral mixing mechanism inside a Vertical Color Mixer typically consists of a vertically oriented screw blade or auger that rotates within a cylindrical mixing chamber. As the spiral turns, it lifts materials from the bottom of the tank and disperses them evenly throughout the volume. This continuous upward and outward flow pattern ensures constant material circulation, allowing all granules or pellets to pass through the blending zone multiple times during a mixing cycle. This efficient internal flow prevents dead zones and eliminates stratification, a common issue with simpler mixing designs.
One of the significant advantages of spiral mixing is the high degree of uniformity it offers in a short amount of time. In traditional paddle mixers, the agitation may not evenly reach all areas of the chamber, leaving some material less blended than others. In contrast, the screw in a Vertical Color Mixer promotes a consistent turnover of material, exposing all components—whether virgin polymer, recycled resin, or color masterbatch—to the same degree of mixing. This results in a uniform color distribution, which is critical in producing visually consistent plastic products.
Another clear benefit lies in energy efficiency. Because of its vertical structure and efficient mechanical design, a spiral mixer requires relatively low power consumption to achieve a mix. Compared to horizontal or rotary drum mixers, which often need longer mixing cycles and more vigorous motion, spiral mixing reduces mechanical stress while improving performance. The reduced energy usage translates directly into lower operational costs and decreased wear on mechanical components, extending the lifespan of the equipment.
The design also lends itself to space-saving advantages. The vertical configuration occupies less floor area, making it ideal for smaller production environments or for integration into larger automated systems. Moreover, spiral mixing allows for easy discharge and residue, thanks to gravity-assisted flow and smooth internal surfaces. This contributes to faster batch changes, easier cleaning, and less cross-contamination between different color or material runs.
When comparing the spiral system to tumble mixers—where the entire mixing chamber rotates—it becomes clear that the latter is more prone to inconsistency, especially in larger batch sizes. Tumble mixing relies heavily on gravitational movement, which can be less effective for materials with different bulk densities or flow characteristics. Spiral mixing, however, uses mechanical force to actively blend materials, which makes it more adaptable and reliable across a wide range of resin types and additive concentrations.
In addition, spiral mixers offer operational simplicity. Most Vertical Color Mixers with this mechanism can be operated with basic controls and minimal training. This is particularly valuable in high-throughput environments where rapid learning curves and consistent machine behavior are necessary. The reduced maintenance requirements, combined with strong output performance, make spiral-based mixers an attractive choice for both small workshops and large manufacturing plants.
Finally, spiral mixing supports better process integration. Whether feeding into an injection molding machine, extrusion line, or granulating system, the uniform output from a Vertical Color Mixer improves downstream process stability. This means fewer rejects, better color matching, and reduced additive waste—all of which contribute to cost savings and improved product reputation.
Recommended Products
-
Modol: Auto Loader-TMAL-300G
TMAL-300G Small Plastic Auto Loader Automatic Material Feeding Machine
 See More
See More 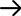
-
Modol: Multi-station-Hopper-Loaders-TMAL
High-Efficiency One-To-Many Hopper Suction Machines Can Be Equipped With 6 Hoppers
 See More
See More 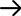
-
Modol: Plastic Auto Loader hopper
Multi-Style And Multi-Standard Adaptive Plastic Auto Loader Hopper
 See More
See More 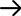
-
Modol: Standard Dehumidifier
Standard Intelligent Rotary Air Dehumidifier For Industrial Use
 See More
See More 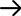


 English
English عربى
عربى




